Object Explorer
1. Introduction
The Object Explorer is a universal resource browser designed to provide a single pane of glass for all Kubernetes resources across your clusters. Whether you are finding, browsing, or managing resources, the Object Explorer offers a unified interface to handle any resource type with ease.
Key Benefits:
- Access all resource types: Native and Custom Resources (CRDs) are fully discoverable.
- Powerful filtering: Drill down by kind, namespace, status, age, and labels.
- Multiple view modes: Visualize data via Grid or List views.
- Bulk operations: Manage resources at scale with ease.
2. Prerequisites
Before using the Object Explorer, ensure you have:
- Kubernetes Cluster Access: An active connection to your target cluster.
- Proper RBAC Permissions: Sufficient rights to list, get, and watch the resources you intend to manage.
- KubeStellar UI Access: Authenticated access to the web interface.
3. Feature Overview
The Object Explorer is built on three core philosophies: universal resource auto-discovery, smart filtering, and adaptable visualization.
3.1 Universal Resource Browser
The browser provides access to all Kubernetes resources, supporting auto-discovery of API groups and versions.
Supported Built-in Types:
- Workloads: Pods, Deployments, StatefulSets, DaemonSets, Jobs, CronJobs, ReplicaSets.
- Network: Services, Ingresses, NetworkPolicies.
- Config & Storage: ConfigMaps, Secrets, PersistentVolumes, PersistentVolumeClaims.
- Access Control: ServiceAccounts, Roles, RoleBindings.
- Custom Resources: Full support for all Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs).
Capabilities:
- Auto-discovery of available resource types.
- Dynamic key listing based on API group detection.
- Full support for both namespaced and cluster-scoped resources.
3.2 Smart Filtering System
A robust multi-variable filtering system helps you isolate resources quickly.
Filter Categories & Features:
- Multi-Kind Selection: Select multiple resource types (e.g., Deployments + Services) via a multi-select dropdown with search and recently used highlights.
- Multi-Namespace Selection: Filter across “All Namespaces” or specific sets, with search and count indicators.
- Status Filter:
Running,Pending,Failed,Succeeded,Unknown. - Label Filter: Add multiple key-value pairs with AND/OR logic and auto-suggestions.
- Age Filter: Presets (Last hour, 24h, 7d, 30d) and custom ranges.
Quick Search:
- Real-time, case-insensitive search by resource name with partial match support.
- Search history and easy “Clear” controls.
Diagram: Filter Flow
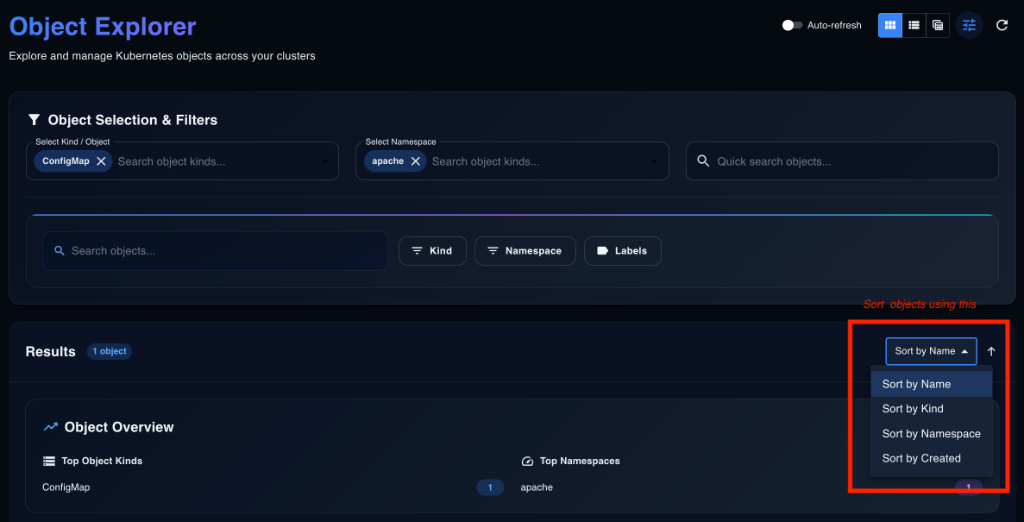
3.3 View Modes 👁️
Switch between modes to suit your workflow. Preferences are persisted locally.
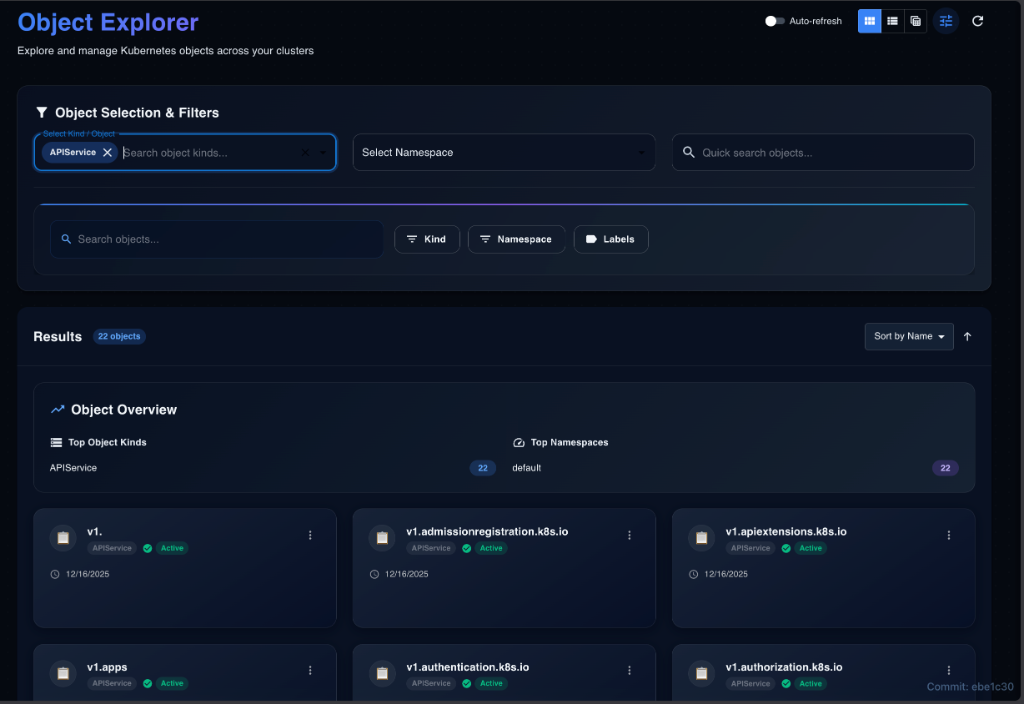
Grid View (Card Layout) Best for: Visual browsing and health checks.
- Card Design: Prominent name, icon/type badge, status indicator, action menu (⋮), and quick stats (replicas, ports).
- Features: Responsive columns, hover effects, and skeleton loading.
List View (Compact) Best for: Scanning large datasets.
- Row Design: Type icon, status dot, age, label count, and action menu.
- Features: Condensed spacing, keyboard navigation, and double-click to view details.
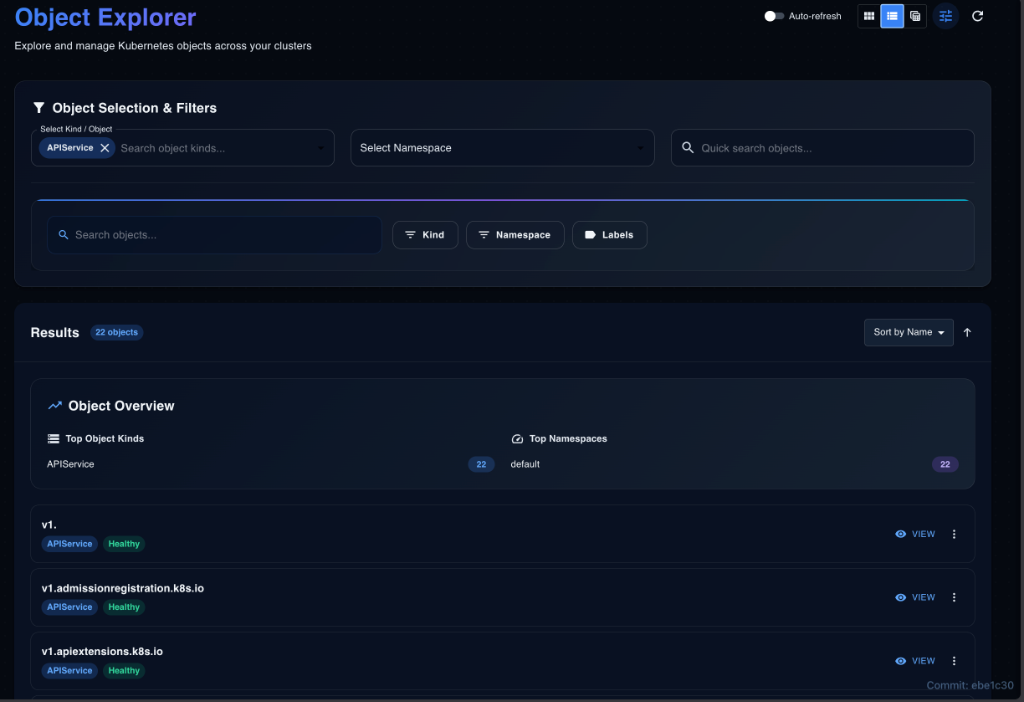
Table View (Future) Best for: Deep analysis.
- Sortable/resizable columns and CSV export.
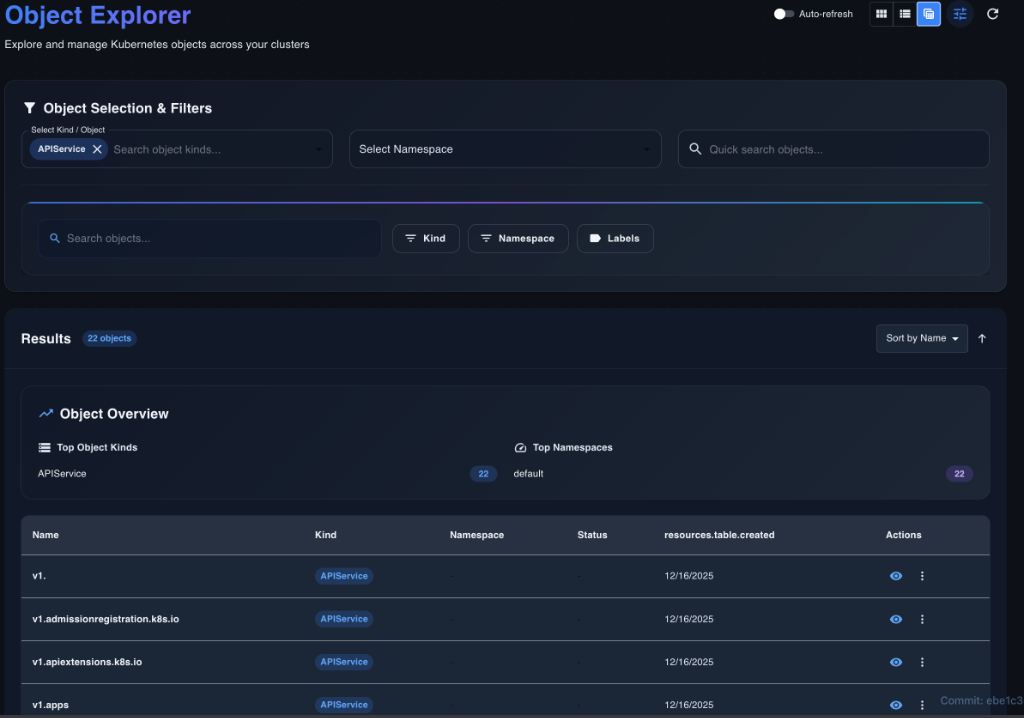
Diagram: View Modes Comparison
3.4 Resource Operations ⚙️
Perform actions on single or multiple resources.
Individual Actions:
- View Details: Opens the detail panel.
- Edit Manifest: In-place YAML editor with validation and save capability.
- View Logs: Live streaming for Pods with container selection.
- Delete: With grace period and cascade options.
- Additional: Describe, Copy Name/YAML, View Events.
Bulk Operations:
- Selection: “Select All” page or matching filters.
- Actions: Bulk delete, bulk export (zip), bulk label update.
- Progress: Real-time progress bar with success/error counts.
Diagram: Bulk Operations Flow
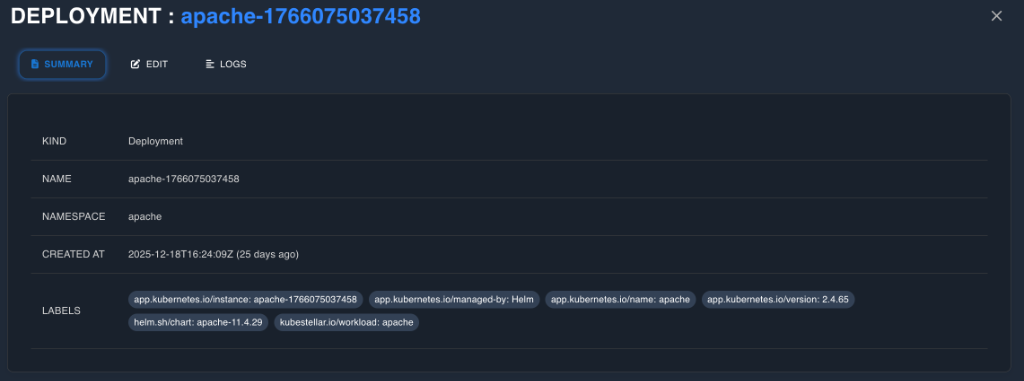
3.5 Resource Detail Panel
A comprehensive slide-out panel for deep inspection.
- Summary View: Metadata, Owner References, Labels/Annotations (editable), and Status Conditions.
- Full Manifest Tab: Complete YAML/JSON with copy/download/edit controls and syntax highlighting.
- Related Resources: Navigable links to Owners (Controllers), Owned resources (Pods), and referencing Services/Ingresses.
- Events Tab: Chronological list of warning and normal events.
3.6 Additional Features
- Auto-Refresh: Toggleable (5s, 10s, 30s, 60s) with pause-on-hover/open.
- Pagination: Configurable page size (25, 50, 100) and jump-to-page.
- Error Handling: Network notifications, permission warnings, and retry options.
- Loading States: Skeleton screens and optimistic UI updates.
- Empty States: Illustrative graphics with action suggestions (e.g., “Create your first resource”).
4. Step-by-Step Guides
Guide 1: Browsing Pods Across Namespaces
- Navigate to
/resources. - Select Pods from the specific Kind dropdown.
- Choose All Namespaces in the namespace selector.
- (Optional) Apply a Status Filter for
Failedto identify issues.
Guide 2: Finding Resources by Labels
- Open the filters panel.
- Add a Label Filter.
- Enter key
appand valuefrontend. - Results will filter to matching resources immediately.
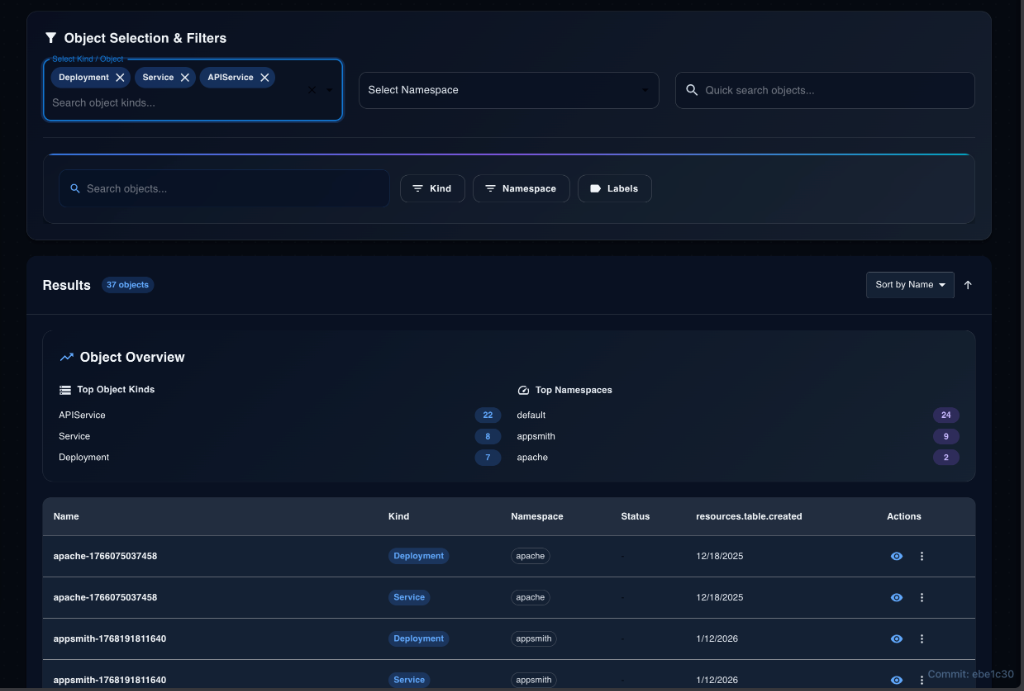
Guide 3: Using Multi-Kind Filtering
- Open the Kind dropdown.
- Select Deployments, Services, and API Service.
- View the combined list to see the full footprint of your application.
Guide 4: Bulk Deleting Resources
- Filter for the resources you wish to remove (e.g., by label
env=test). - Check the Select All box.
- Click Bulk Actions > Delete.
- Confirm the action in the dialog.
Guide 5: Editing Resource Manifests
- Click the Action Menu (⋮) on a resource.
- Select Edit Manifest.
- Modify values in the Monaco Editor.
- Click Save.
Guide 6: Viewing Resource Details
- Click the resource name or card.
- The Detail Panel opens.
- Switch to Events to see recent activity or Manifest to see the live config.
5. Use Cases
Use Case 1: Debugging Across Namespaces
Scenario: An application is failing, but the specific namespace is unknown.
Solution: Filter Kind to Pod, Namespace to All, and Status to Failed. Use Quick Search for the app name.
Use Case 2: Auditing ConfigMaps and Secrets
Scenario: You need to audit configuration resources created in the last month.
Solution: Filter Kinds to ConfigMap + Secret. Set Age Filter to Last 30 days.
Use Case 3: Cleaning Up Unused Resources
Scenario: A development environment needs to be torn down.
Solution: Filter by Namespace dev-env. Select all resources. Perform Bulk Delete.
Use Case 4: Discovering Custom Resources
Scenario: Exploring a newly installed Operator. Solution: Open Kind dropdown. Search for the Operator’s group. Select the new CRDs to explore instances.
6. API Reference
Endpoints:
GET /api/v1/resources: List resources. Supportskind,namespace,labelSelector,fieldSelector.GET /api/v1/resources/{kind}/{namespace}/{name}: Get single details.PUT /api/v1/resources/{kind}/{namespace}/{name}: Update resource.DELETE /api/v1/resources/{kind}/{namespace}/{name}: Delete resource.
7. Troubleshooting
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Permission Errors | Missing RBAC. | Request list/watch permissions from admin. |
| Slow Loading | Large dataset. | Filter by namespace or reduce page size. |
| Filter Not Working | Typo in label. | Check label syntax key=value. |
| Empty Results | No matches. | Clear filters and retry. |
8. Related Features
- WECS: Use Object Explorer to verify WECS deployments.
- ITS & WDS: Integrated monitoring of inventory and workload descriptions.